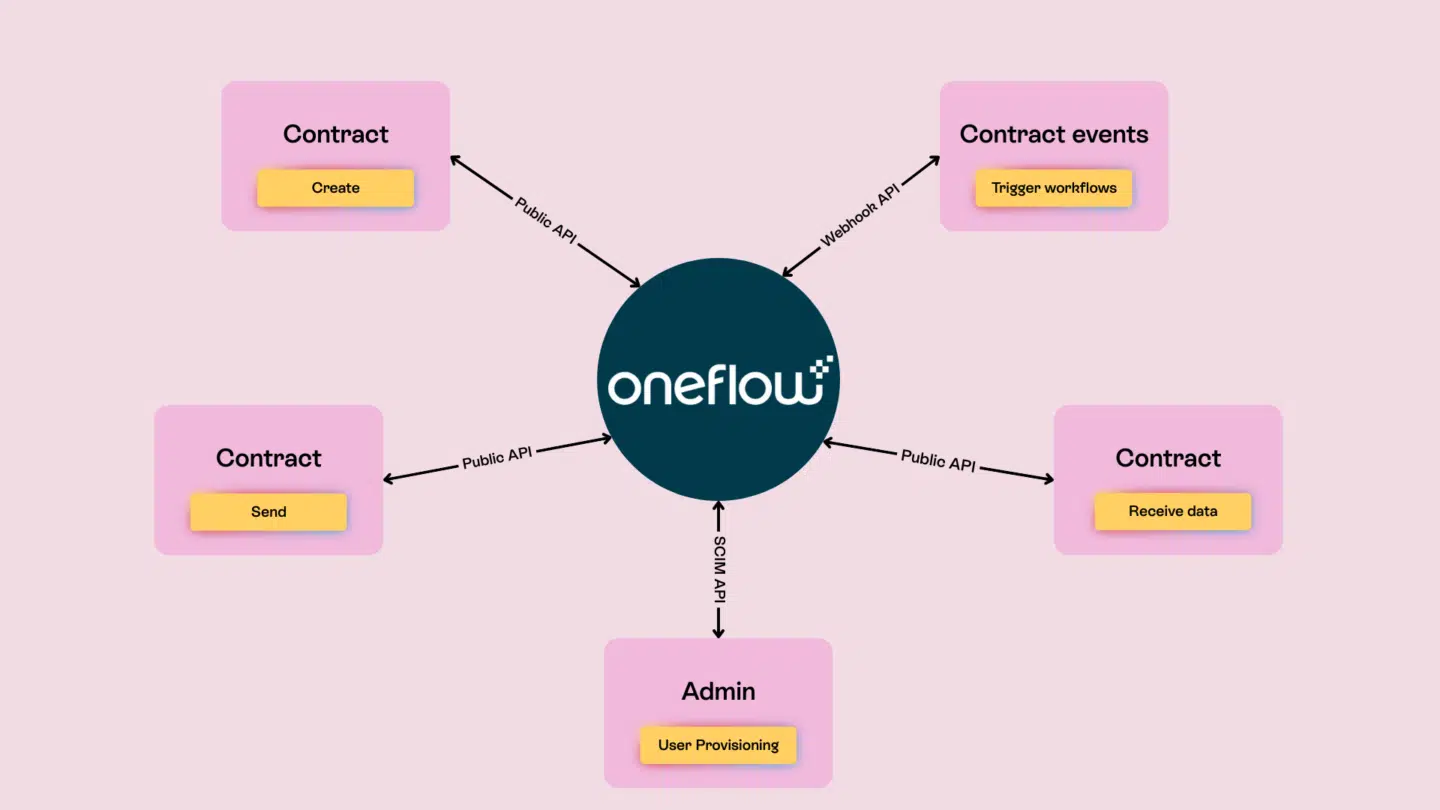
According to Eurostat, in 2024, 74% of all European Union (EU) businesses had a basic level of digital intensity. It’s an indicator that measures progress in adopting digital technologies, including electronic transactions and digital signature solutions. The latter are especially important because they pave the way towards a world where you sign contracts with a click, minimize disputes, and achieve rock-solid legal validity. If you’re still printing, signing and scanning documents with a handwritten signature in 2026, you might as well be sending messages by carrier pigeon.
However, digital signatures are a complex topic, and understanding the difference between the “advanced” and “qualified” variants can be a challenge. This guide will demystify advanced electronic signatures, explain how they compare to their “qualified” alternatives, and demonstrate why getting this right can help you avoid problems in the case of a legal dispute over a high-value contract.
See also: How to take the next step in your digitalization journey
What is an advanced electronic signature (AdES)?
An Advanced Electronic Signatures (AdES), as defined under the eIDAS Regulation (EU Regulation No 910/2014), is a signature in an electronic form that meets the following requirements that the law requires to ensure the signature’s reliability and legal standing:
- Uniquely linked to the signatory: An AdES signature is tied exclusively to the person signing.
- Capable of identifying the signatory: You can verify the signer’s identity without a doubt.
- Created using electronic signature creation data that the signatory can use with high trust: The AdES signature needs to work in such a way that the signer has sole control over the signing process, typically achieved by using a unique key (private key).
- Linked to the signed data so that any changes are detectable: Any alterations to the document after signing will be evident, therefore invalidating the signature.
AdES commonly employs technologies such as digital certificates and encryption and implements AdES Baseline Profiles—defined by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)—to meet these criteria.
Advanced vs. qualified electronic signature: What’s the difference?
While both Advanced and Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are legally valid under eIDAS, there are key distinctions between them. QES has a higher probative value, meaning it carries more weight during legal proceedings—in fact, it’s automatically recognized in court. It also employs stricter identity verification methods and requires a digital signature certificate (just like AdES), plus a qualified one and a trust service verified by a certificate authority.
Here’s a summary table that explains the differences clearly:
| Feature | Advanced Electronic Signature (AdES) | Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) |
|---|---|---|
| Legal validity under eIDAS | Yes | Yes (with higher probative value) |
| Requires a qualified certificate? | No | Yes |
| Requires a qualified trust service? | No | Yes (e.g., listed in EU Trust List) |
| Identity verification method | Flexible (a unique access code sent to the signer’s email address, signer’s ID verification, passport or driver’s license, etc.) | Strict (face-to-face or remote with KYC-compliant methods) |
| Common use cases | Internal contracts, HR docs, NDAs | Cross-border B2B contracts, high-value legal contracts |
| Legal presumption of authenticity? | No | Yes (automatically recognized in court) |
When is an advanced electronic signature enough in the EU?
Advanced Electronic signatures (AdES) are legally sufficient for many common business use cases, including:
- Employment contracts: An Advanced Electronic Signature provides sufficient legal validity within the EU in most routine employment scenarios, such as contracts for hiring new employees and amendments to existing contracts. It ensures you can verify the employee’s identity and guarantees the contract’s integrity.
- NDAs: AdES is usually sufficient for signing NDAs because it ensures both parties are who they claim to be, and the document can’t be tampered with by linking the signature to the legitimate signatory and the specific data of the NDA, allowing for instant detection of alterations.
- Vendor agreements: Basic vendor agreements (especially of low or medium value), purchase orders and service contracts are often appropriately secured with AdES. It helps ensure that you can identify all parties and detect any changes to the agreement after signing.
- Internal policies: You can also use AdES to handle internal policies, including codes of conduct, IT policies and compliance guidelines. The key feature here is the audit trails, which are essential for demonstrating policy compliance and accountability within the organization.
AdES is a cost-effective and legally valid choice for most day-to-day business processes, offering a good balance between security, usability and cost. However, higher-risk transactions (involving significant financial commitments, sensitive personal data or critical intellectual property), may require a QES signature, which—in practical terms—is a legal equivalent of an, in-person, handwritten signature. When choosing the signature type, consider the entire situation, including the transaction value, and any applicable national legal requirements.
See also: How to enhance your contract security and data privacy
Why use an advanced electronic signature?
An advanced electronic signature offers significant advantages over a simple (basic) electronic signature:
- Enhanced security: Digital certificates and encryption protect the integrity of the document and signatory data, making it less likely to be tampered with and safeguarding the information within.
- Clear signatory identification: AdES lets you identify the signatory. This verification reduces the risk of fraud or misrepresentation.
- Stronger legal validity: An advanced signature has a stronger legal standing compared to a simple electronic signature. Because it uniquely links the signature to the signatory and makes any alterations detectable, it’s more reliable as evidence in legal disputes, and the probability of denied legal effect is lower.
- Operational efficiency: Implementing AdES can eliminate the need for physical paperwork and manual signing. Digitization enables faster turnaround times, lowers costs, and enhances efficiency without compromising security and compliance.
- Increased trust and confidence: AdES serves as a common foundation that helps you build trust with business partners and customers. When stakeholders know that they sign agreements with a legally binding and secure method, they are more likely to have confidence in the transaction.
See also: Contract creation: The only guide you need
How to choose between advanced and qualified signatures
Choosing between Advanced (AdES) and Qualified (QES) Electronic Signatures depends on several critical factors. Here’s a more detailed look at what to consider:
- Legal risk of the transaction: Assess the potential consequences if someone challenges the signed document. High-value transactions, significant financial commitments, deals involving critical intellectual property, or agreements with sensitive data carry higher legal risks. In such cases, the higher probative value of QES might be necessary to ensure enforceability and minimize risk.
- Counterparty jurisdiction: Determine the location and legal framework of the counterparty (a person or a legal entity). If the agreement involves parties in different countries, especially outside the EU, the recognition and acceptance of different electronic signature types can vary widely. While eIDAS provides a harmonized framework within the EU, relying on QES offers greater assurance in international transactions, some jurisdictions may not fully recognize AdES; on the other hand, QES, with its higher level of security and authenticity, is more likely to be accepted universally.
- Cost and onboarding effort: Consider the financial and logistical implications of implementing each type of signature. AdES solutions are typically cheaper and easier to implement, requiring less rigid identity verification. QES systems can be more expensive due to the need for qualified certificates and qualified trust service providers. Additionally, the stricter identity verification for QES might require more time and effort for you and your counterparties.
- Regulatory compliance needs: Verify any specific regulatory requirements applicable to your industry or the particular transaction. Certain regulated sectors, such as finance, healthcare or government, may have strict rules mandating the use of QES for specific types of documents or procedures.
See also: Discover the best practices for contract compliance
Best tools for secure e-signing: Oneflow
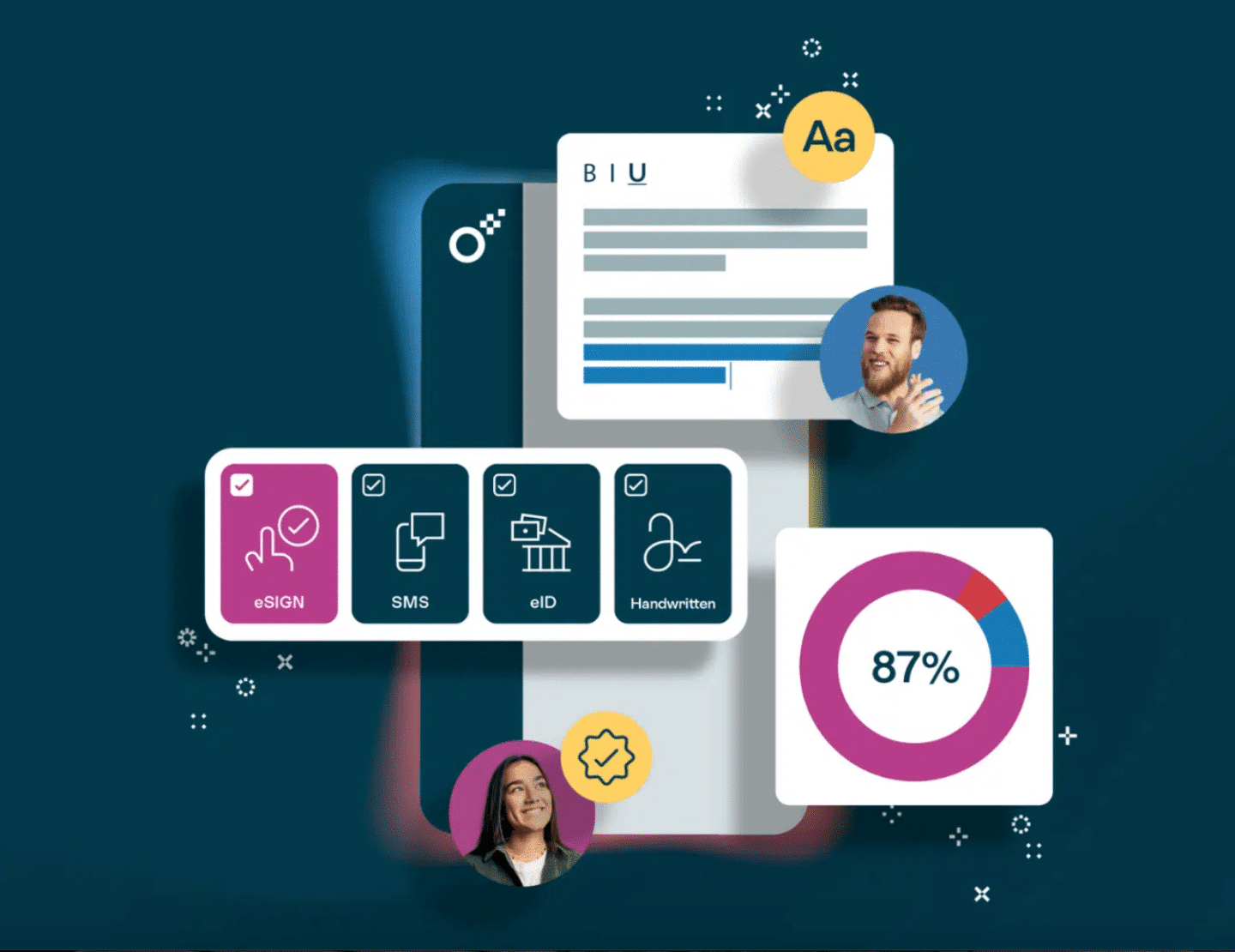
Oneflow is a comprehensive contract lifecycle management software that offers full compliance with the AdES and QES formats. We created it to optimize and enhance every stage of the contract process, from initial drafting through execution and ongoing management. The solution provides a centralized contract repository, along with legally binding electronic signature options that include digital signatures, electronic identification, standard e-signatures, SMS verification and traditional wet-ink signatures.
Oneflow enhances contract management through automated, customizable signing workflows with valuable post-signing functionalities such as document linking and data extraction. The platform also features collaboration tools and advanced AI capabilities for faster draft creation and review. All these features are integrated into a user-friendly platform with extensive integration options.
Here is Oneflow’s feature set:
- Centralized database—Store all your contracts in Oneflow’s central database for easy contract lifecycle management. Use powerful organization tools, including search, filters, folders, tags, document roles and a calendar view with lifecycle milestones.
- Powerful security—Manage user roles and assign them specific permissions (editing, viewing, etc.) to control and restrict access to documents. Ensure your contracts are reliably protected with powerful encryption (TLS 1.2 and AES 256) and verify counterparties’ identities with two-factor authentication. We know that identification is an integral part of the signing process—if it fails, the contract won’t be signed. You can also use audit trails to track any subsequent change made to the document and secure it with an electronic seal after signing.
- Compliance and reliability—Capitalize on Oneflow’s full compliance with eIDAS (EU) standards. Configure custom data retention policies to ensure GDPR compliance. We built Oneflow on a redundant infrastructure for perfect business continuity. As of July 2024, it is also certified in Information Security (ISO 27001), Quality Management (ISO 9001), and Environmental Management (ISO 14001).
- Real-time collaboration—Enhance contract collaboration with comments, configurable triggers, detailed audit trails and secure, branded workspaces. These features ensure efficient collaboration without the confusion of multiple versions. Oneflow verifies the identity of everyone working on documents and locks specific sections to protect them from unauthorized changes.
- Signing order—Customize the signing sequence to fit different business scenarios or account for various roles, document types and other factors.
- Lifecycle management—Manage your time effectively with personalized notifications for contract openings and the integrated calendar to ensure you always meet important deadlines.
- Seamless integrations—Integrate with any solutions you’re currently using, including Google Drive as well as HubSpot, Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics CRM systems. For more details, check out our dedicated articles on Contract management software in Salesforce and Electronic signatures for Hubspot.
- Oneflow AI and contract automation—Use Oneflow’s AI in contract work to improve contract workflows via automated reviews that detect errors and compliance gaps based on your legal guidelines. Save time and effort with AI assistance for drafting, editing and instantly summarizing or translating your documents.
- Post-sign processes—Archive contracts in Oneflow and extract metadata for better tracking and insights across all data, specific folders or workspaces. You can also link related internal documents and add external URLs.
- Dynamic templates—Use our free, fully customizable contract templates to quickly generate agreements or create personalized templates for future efficiency.
- Analysis—Gain insights from engagement data and metrics, including document open rates and visitor numbers.
Interested in Oneflow? Check it out now with our 14-day free trial!
Future-proof your contract workflow with Oneflow
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AdES) provide a secure and efficient way to sign documents electronically, offering a balance between security and ease of use. However, QES carries greater legal weight and requires stricter verification. This higher assurance level is great for high-value scenarios.
Oneflow is a comprehensive platform that supports both AdES and QES, streamlining the entire contract lifecycle from drafting to execution and management. With a strong focus on security and compliance, and features such as centralized storage, AI assistance, collaboration tools, identity verification and seamless integrations, Oneflow sets the gold standard for secure and efficient e-signing.
Want to future-proof your contract workflow and experience the benefits of Oneflow’s AdES and QES capabilities? Sign up for a 14-day free trial!
FAQs
What is an advanced electronic signature?
An electronic signature that meets specific legal criteria under eIDAS, ensuring it’s uniquely linked to the signatory and capable of identifying them.
How do I get an advanced electronic signature?
The easiest way is to use a trusted electronic signature solution like Oneflow, which provides AdES capabilities.
Is Docusign an advanced electronic signature?
Yes. Docusign offers various levels of electronic signatures, including some that meet AdES requirements.
What is the difference between a qualified electronic signature and advanced electronic signature?
QES requires a qualified certificate and a qualified trust service and has a higher legal presumption of authenticity compared to AdES.