Home > What are digital signatures? A complete guide for 2025
What is a digital signature? A complete guide for 2025
What are digital signatures? A complete guide for 2025

Ever been stuck trying to sign or send an important document digitally, unsure if you’re even doing it right? I’ve been there—early in my remote work days. One word describes that feeling perfectly—frustrating. But, like most missteps do, they taught me a lot.
Now, I want to ensure you don’t go through the same struggle—or ever have to deal with it again.
The answer?
Digital signatures.
As I write this, it’s almost 2025, and let’s be honest—digital signing isn’t going anywhere. In fact, you’ll probably be using it even more.
This guide breaks it all down: what digital signatures are, how they work, and why they matter. I’ll also show you how to create them easily and securely. Plus, I’ll introduce you to Oneflow, a tool that helps you stay on top of your signatures and contracts.
What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is a virtual stamp that proves who sent a digital message or file and that it hasn’t been tampered with. It verifies the sender’s identity and the integrity of the digital document, making it legally binding.
It works like a pair of keys. Both the sender (the person or company who creates and sends the contract) and the receiver (the one who must sign the document) each have a pair of keys:
- Private key: Used to create the digital signature (and kept only by you).
- Public key: Used by others to verify the digital signature. You share it with anyone who needs to verify your signature. If you use an e-signing platform like Oneflow, your public key cryptography can be automatically made available to the other party through the platform.
The sender uses their private key to create a digital signature, which is a unique code linked to that document. This code serves as a personal seal, proving the document is genuinely from the sender. The receiver uses the sender’s public key to verify the signature. If the code matches, it confirms that the document and signature are authentic and unchanged.
This is crucial for online data security and trust because it ensures that information comes from the right source and hasn’t been altered after signing.
See also: How to digitize a signature?
What is the difference between an electronic signature and a digital signature?
At first glance, electronic signatures and digital signatures might seem like the same thing, but they’re not!
Here’s the key difference to remember:
- An electronic signature is a broad term for any electronic process that signifies agreement to a document or contract. This may be clicking an “I agree” button or typing your name into a signature field.
- On the other hand, a digital signature is a specific type of electronic signature that uses encryption technology to verify the signer’s authenticity. It ensures that the document wasn’t altered since signing.
Here’s a more detailed overview of their differences:
| Digital signature | Electronic signature |
|---|---|
| A digital signature ensures the integrity and authorship of your contracts. | An electronic signature ensures the signature is connected to the signer. |
| A digital signature ensures your signed contracts are tamper-proof, preventing changes after they’re signed. | An electronic signature indicates that the signer agrees to the contract. |
| A digital signature is a method to guarantee integrity. | An electronic signature is a type of signature. |
| A digital signature is generated by software technology. | An electronic signature is generated by the signer either through a click of a button or a hand-drawn signature on an electronic device. |
How do digital signatures work?
Digital signatures work the same way that handwritten signatures do. They’re unique to each person. But when signing digitally, we can’t always see the other party signing in real time, or track document changes.
This is why we need a system to guarantee authenticity—Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
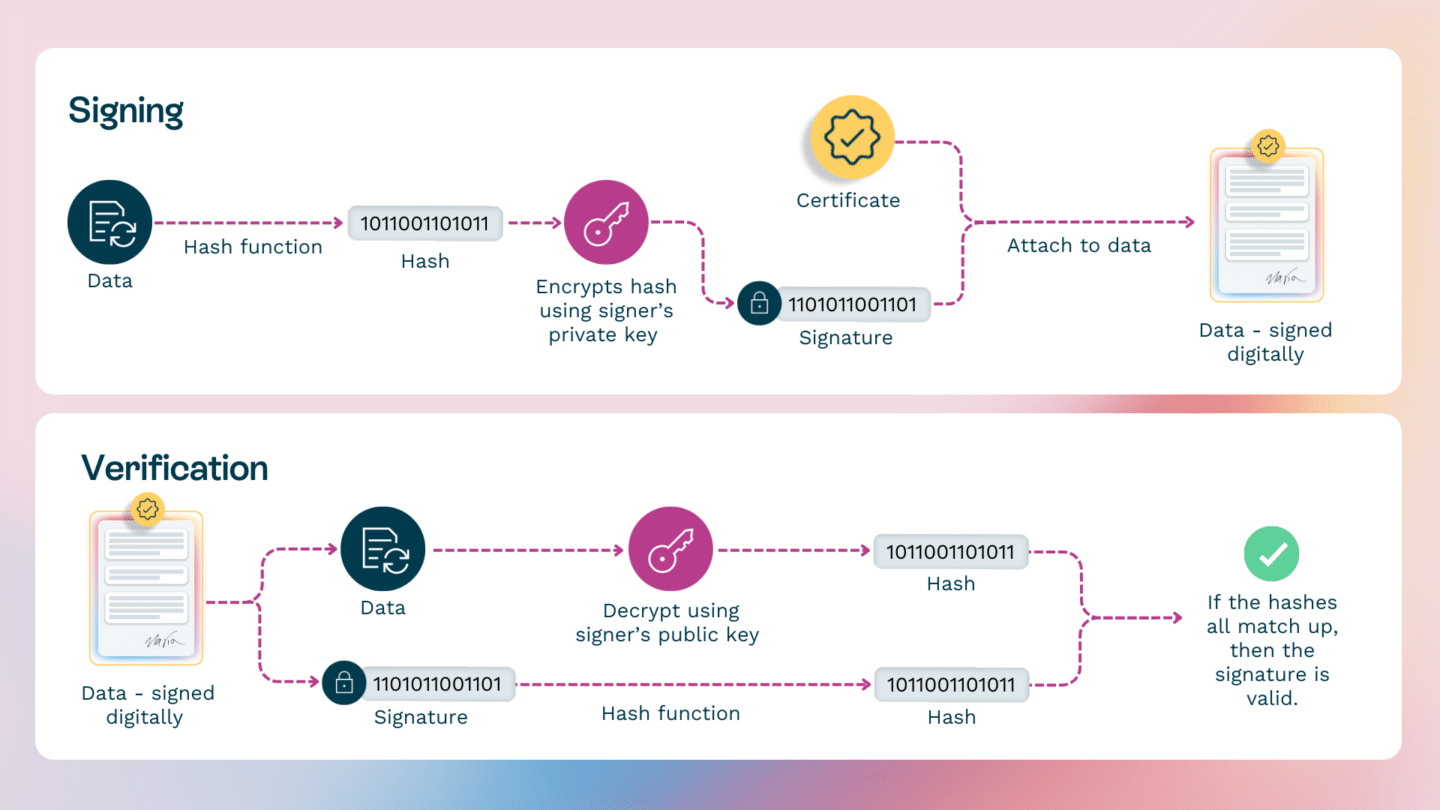
It’s a set of rules and technologies that enable the creation of digital signatures. The pair of keys we mentioned earlier are one of those requirements. Others include the digital certificate and the tools and algorithms for encrypting and verifying the signature.
This is how these PKI-enforced elements work together every time you sign a document electronically.
The whole process happens inside an e-signing tool that follows digital signature PKI standards. First, the tool creates a unique representation of the document’s contents, known as a hash function. Then, your private key locks that hash into place, forming your digital e-signature.
To ensure your e-signatures can be verified, the e-signing platform shares your public key. Others can use it to check the signature against the document’s hash. If it matches, they know the document is authentic.
A time stamp adds another level of digital signature security—it shows the exact moment it was made. If someone tries to change the document after signing, the digital signature won’t match anymore, making it invalid.
Another essential Public Key Infrastructure requirement for digital signatures is the digital certificate. It further helps maintain the security and authenticity of the signature.
What are digital certificates?
A digital certificate, or a digital signature certificate, is an electronic document used to verify the identity of a person, organization or device. It contains information about the entity it belongs to, including their public key, name and other identifying details.
Digital certificates secure digital signatures for online transactions, such as e-commerce transactions, online banking and secure email communication. They also secure network connections and authenticate users accessing a network.
Digital certificates are issued by trusted third-party organizations known as Certificate Authorities (CAs), which verify the entity requesting the certificate and issue it once the verification process is complete.
What is a Certificate Authority (CA)?
A Certificate Authority (CA) is a trusted entity that issues digital certificates, validating the authenticity of websites or users. It ensures secure online communication by confirming the parties’ identities and safeguarding against fraud and eavesdropping.
Digital signature vs. Digital certificate
Let’s quickly recap the differences between a digital signature and a digital certificate to avoid confusion.
Digital signatures create a virtual fingerprint. They’re a secure way of verifying the authenticity and integrity of a contract. They tell you the content wasn’t altered and verify the sender’s private key and identity through encryption techniques.
A digital certificate is an electronic document issued by a trusted authority (Certificate Authority) that verifies the ownership of a public key. It contains the owner’s public key and other identifying information, ensuring that communications between parties are secure and trustworthy.
In other words, a digital certificate proves who you are, but adding it doesn’t necessarily mean you’ve agreed to the contract. While related, these two concepts play different roles in ensuring the authenticity and integrity of signatures and digital documents.
See also our guide on digital handshakes.
How do I create a digital signature?
With the basics covered, it’s time to get to the actual signing!
First and foremost, you need an e-signing tool that complies with Public Key Infrastructure standards. This ensures its algorithm guarantees the security and authenticity of your signatures and documents.
One such tool is Oneflow.

It’s a digital contract automation platform that meets all the PKI requirements for safe and secure digital signatures. Oneflow works with digital signing certificates and uses PKI-compliant algorithms to ensure public and private key verification.
With Oneflow, you can create digital signatures confidently, knowing they are both secure and valid.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for electronic ID signing with Oneflow:
- Create a free Oneflow account.
- Click on the Marketplace. Select the Electronic ID and Enable

- Select the electronic IDs you want to activate. Options include Swedish BankID, itsme, Smart-ID and more. See the complete list of Electronic IDs we offer.

- Click on the + New document on your dashboard to create your document.

- Once in the document, on the right-hand side, select Add a counterparty. Fill in all necessary information, go to the Sign Method section and select the electronic ID you want to use.

- When it’s time to sign, click the Sign button and follow the instructions from your electronic ID provider.

Congrats! You’ve signed a document with an electronic ID!
But there’s more you can do with Oneflow.
Besides making digital signatures super easy, the platform simplifies creating and managing contracts. Our advanced AI tools help you draft documents and catch errors so you can avoid slipping up on important details or leaving out key clauses.
Oneflow offers a rich library of free templates, covering everything from agreements for obtaining digital signatures for car rentals to marketing proposals. You can also create custom templates tailored to your business needs.
Collaboration is easy within the platform, too. Teams can stay connected at every step of the signing and contracting process, share comments and get notifications about updates. You can set permissions and enable advanced security features like two-step verification and single sign-on to make your digital signatures secure and authenticate your documents.
Ready to give it a go?
8 benefits of digital signatures
Digital signatures are not only more secure than traditional signatures, but they can also improve workflow efficiency.
Faster document processing
Traditional signatures require printing, signing, scanning and emailing or mailing documents, which can take considerable time. With digital signatures, you can sign documents instantly, reducing the time it takes to process documents.
Remote signing
Digital signatures allow you to digitally sign documents from anywhere worldwide, as long as you have an internet connection. You don’t have to be physically present to sign documents, making it easier to complete transactions with clients and partners in different locations.
Automated workflows
Digital signatures can be integrated into automated workflows, streamlining document processing and helping in managing digital signatures-related risks like missing deadlines. Automated workflows can send reminders to signers.
Increased security
As previously mentioned, digital signatures are more secure than traditional signatures. They use encryption technology to verify the signer’s authenticity, making it difficult for forgers to create fraudulent electronic signatures.
Reduced costs
Digitization reduces the costs associated with printing, scanning and mailing documents. It also reduces the need for physical storage of documents.
Uniqueness
Your handwritten signature is only yours and should be hard to copy. A digital signature is even more uniquely yours. Thanks to PKI, private and public keys and digital certificates, every signature contains identifying information specific to each signer.
Global acceptance
PKI-based digital signatures are standard for institutions, governments and organizations around the world. For example, you can sign a contract in the USA, and your partner in Germany can verify its authenticity instantly.
Tamperproof seal
Once a document is signed with a digital signature, it’s sealed. Any changes made to electronic documents afterwards invalidate the original signature.
How do different industries use digital signatures?
Multiple industries use Oneflow and its digital signature capabilities.
Consulting
Encrypted electronic signatures streamline contract management, enabling consultants and clients to sign documents electronically. This eliminates paperwork and accelerates the document signing process for engagement letters, proposals and non-disclosure agreements while maintaining legal validity and creating an audit trail.
Recruitment
Digital signatures make recruitment faster and simpler. Candidates can sign documents from anywhere, which is perfect for remote roles. This also helps eliminate printing, scanning and mailing, saving time and resources.
Tech and software
The tech industry relies on digital signatures for software authenticity and integrity. Developers digitally sign software packages and updates to verify their genuineness and protect against malware. These signatures are also used in contracts, licensing agreements and intellectual property protection, facilitating secure collaborations within the tech sector.
Construction
Digital signatures speed up contract management processes in the construction industry. The project manager and contractor can complete the process in just a few clicks. The project manager creates and sends the contract, and the contractor digitally signs it—fast and secure. No more dealing with piles of paperwork or waiting forever for documents to arrive. There’s also no need to worry about losing important papers as everything is stored electronically.
Utilities & energy
“Time is money” is especially true for utilities and energy companies. These businesses make fast decisions and need documents signed quickly while keeping everything secure. Digital signatures make this happen. They let documents be signed from anywhere and keep all information safe. This cuts down on delays and prevents documents from getting lost.
Hospitality
Hotels, restaurants and travel agencies use the digital space to handle customer interactions and services. With digital signatures, they can quickly verify identities and complete remote arrangements. This means customers don’t need to be there in person, making the whole process smoother and more efficient for everyone.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing products often involves negotiating and signing contracts with multiple parties. For example, to create a new product, a business may need to hire contractors, arrange a deal with suppliers for materials and sign agreements with retailers. Digital signatures help speed up these processes—every contract can be signed in minutes, allowing everyone to focus on their tasks without wasting time printing, scanning and sending documents.
Retail
The retail industry comes with tons of paperwork and constant signings. Every new supplier or recipient requires contracts. Digital signatures speed up this process, letting everyone sign from their location without meetings or mailing. They also ensure that documents remain unchanged.
Non-profit
Digital signatures help non-profits save time and money while simplifying document processes. Organizations in this industry often operate with limited resources in staff and funds, making digital signatures a huge help. Managing and storing documents is easier and more cost-effective when they’re signed digitally, as it eliminates the need for paper, printers and mailing. Everything can be handled online with just a few clicks and by one person.
Besides these, digital signatures are useful for many other industries, including:
- Real estate
- Healthcare
- Banking
- Education
- Media and entertainment
- Finance
Secure your digital signature with Oneflow
Digital signatures do much more than let you sign documents remotely. They save time, reduce the risk of losing important documents and ensure everything you sign is valid and tamper-proof.
That’s why it’s crucial to keep your signature safe and secure at all times.
With Oneflow’s PKI-certified and easy-to-use software, you can do this—and also streamline your entire document workflow.
Oneflow AI tools help you draft and analyze contracts, reducing errors and saving time. You can choose from a rich contract template library or create custom ones that fit your needs, speeding up future contract creation. Our collaboration tools minimize confusion and ensure you always know which version is the right one.
Stay in control of your documents—from creating digital signatures to managing contracts—all within Oneflow’s secure platform.
FAQs
How do I create a digital signature?
You can create a digital signature in Oneflow in just a few clicks. Once you’re in a document that you have to sign, simply choose your preferred method. You can either draw your signature using your mouse or type your name and select a font for your signature.
What is a digital signature with an example?
A digital signature is an encrypted signature that verifies the authenticity of a document and the person who signed it. For example, when you sign a contract digitally, your unique digital signature is created using a private key. This signature is then attached to the document. When the recipient receives the contract, they can use your public key to verify that the signature and document are valid.
Can I get a free digital signature?
Yes, you can get a free digital signature. Oneflow offers a 14-day free trial that lets you experience the entire platform, including the ability to create digital signatures.
What are the three types of digital signatures?
Three types of digital signatures are simple, advanced and a qualified electronic signature. All require some authentication. Simple digital signatures usually call for using a private key. On the other hand, qualified digital signatures demand the highest level of authentication.
Jump to section
Book a demo of Oneflow
Book a demo of Oneflow
"*" indicates required fields







