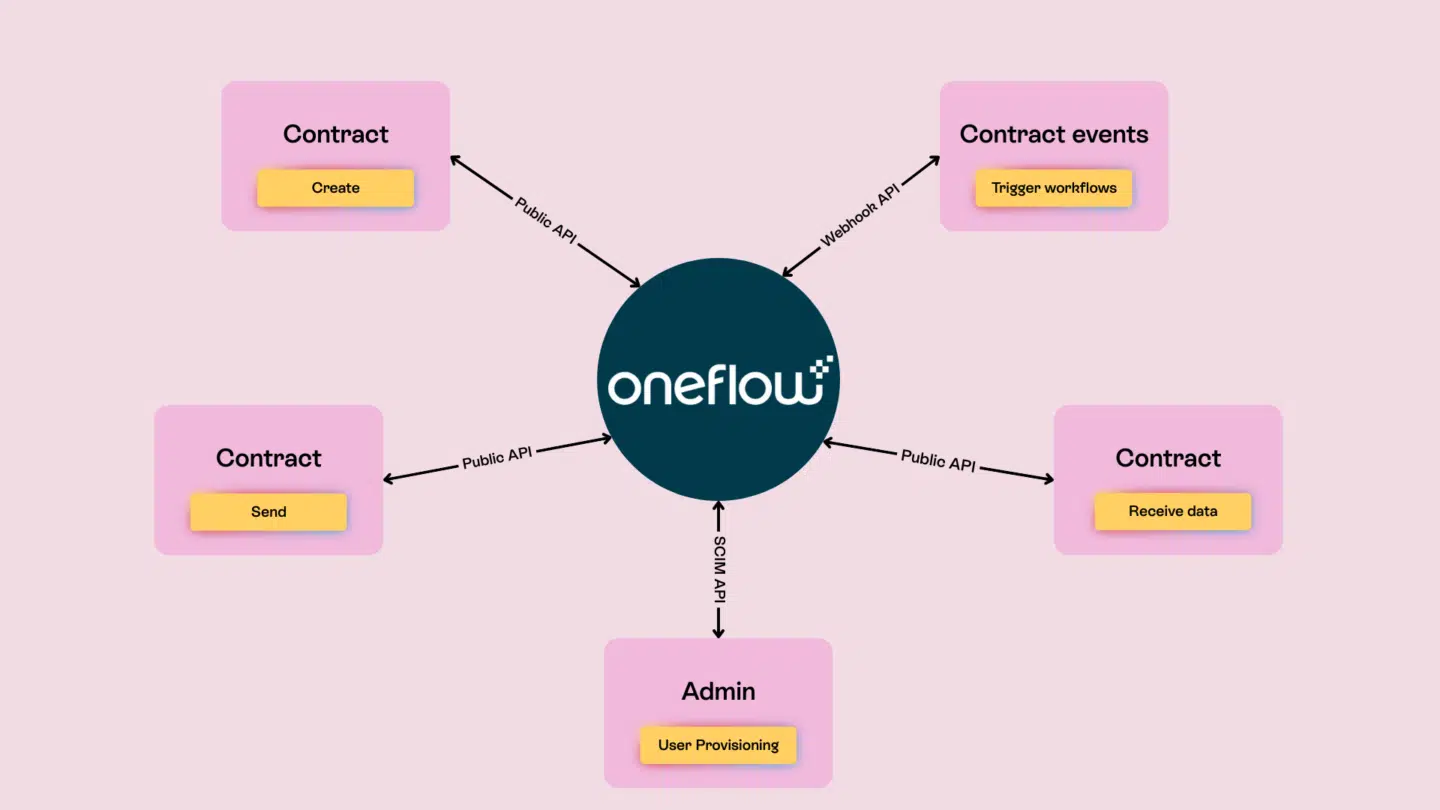
The construction industry, traditionally reliant on paper-based processes, is historically among the slowest to adopt digital technologies. The R&D spending in construction running well behind that of other industries – less than 1% of revenues, compared to 3.5% to 4.5% for the auto and aerospace sectors.
However, recent trends indicate a shift towards digitalization, driven by the need for increased efficiency and productivity.
Construction companies such as STARK and Renta have adopted Oneflow’s digital contract solutions for the construction industry to achieve greater operational efficiency, improved customer experiences, and seamless integration with their existing systems.
In this article, we explore the top 20 documents in the construction industry that can be digitally signed, detailing their importance and how they contribute to streamlined operations.
List of digital signature use cases for construction contracts

1. Construction contracts
- What it is: Agreements between contractors and clients defining project scope, timelines, and payment terms
- Why it matters: Ensures all parties are aligned on expectations, reducing disputes
- Who creates it: Project managers or legal teams
- Who signs it: Contractors, clients, and subcontractors
- Customization: Tailored to each project with standard legal terms
2. Change orders
- What it is: Documents authorizing alterations to the original project scope
- Why it matters: Tracks changes to avoid miscommunication about costs and timelines
- Who creates it: Project managers or site supervisors
- Who signs it: Contractors and clients
- Customization: Highly specific to each project change
3. Subcontractor agreements
- What it is: Contracts defining responsibilities and payment terms for subcontractors
- Why it matters: Clearly outlines roles and minimizes legal risks
- Who creates it: Contractors or legal teams
- Who signs it: General contractors and subcontractors
- Customization: Standard terms with role-specific details
Read also: Top 20 contracts in the manufacturing industry you can sign digitally
4. Purchase orders
- What it is: Documents detailing the materials or equipment purchased for a project
- Why it matters: Ensures accurate procurement and budget tracking
- Who creates it: Procurement teams
- Who signs it: Contractors and suppliers
- Customization: Specific to ordered items and quantities
5. Work orders
- What it is: Instructions outlining tasks for a specific job
- Why it matters: Assigns responsibilities clearly, ensuring tasks are completed on time
- Who creates it: Site supervisors or project managers
- Who signs it: Supervisors and workers
- Customization: Tailored to each task

6. Safety compliance forms
- What it is: Documents ensuring adherence to safety regulations on-site
- Why it matters: Protects workers and ensures legal compliance
- Who creates it: Safety officers or management
- Who signs it: Workers and supervisors
- Customization: Standard forms with site-specific information
7. Permits and approvals
- What it is: Government-issued permissions for construction work
- Why it matters: Ensures projects comply with local regulations
- Who creates it: Local authorities or permitting agencies
- Who signs it: Contractors and inspectors
- Customization: Standardized but specific to the project
8. Timesheets
- What it is: Records of worker hours and attendance
- Why it matters: Tracks labor costs and ensures accurate payroll
- Who creates it: HR or site supervisors
- Who signs it: Workers and managers
- Customization: Standard format, customized for each employee
9. Equipment rental agreements
- What it is: Contracts for renting construction equipment
- Why it matters: Ensures proper use and accountability for rented assets
- Who creates it: Procurement teams or equipment providers
- Who signs it: Contractors and rental companies
- Customization: Standard templates with project-specific details
10. Insurance certificates
- What it is: Proof of liability, property, or workers’ compensation coverage
- Why it matters: Protects against financial risks and ensures compliance
- Who creates it: Insurance providers
- Who signs it: Contractors or project managers
- Customization: Standardized but tailored to each project
11. Bid proposals
- What it is: Documents submitted by contractors to win project bids
- Why it matters: Outlines costs, timelines, and capabilities
- Who creates it: Contractors or estimators
- Who signs it: Contractors
- Customization: Tailored to each project opportunity
12. Payment applications
- What it is: Requests for payment based on work completed
- Why it matters: Keeps cash flow consistent and project finances transparent
- Who creates it: Contractors or project managers
- Who signs it: Clients and contractors
- Customization: Project-specific with standard financial details
Read also: 10 best contract lifecycle management software solutions in 2026
13. Inspection reports
- What it is: Records of site visits and compliance checks
- Why it matters: Ensures quality control and regulatory compliance
- Who creates it: Inspectors or supervisors
- Who signs it: Inspectors and contractors
- Customization: Standard forms with site-specific notes
14. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs)
- What it is: Contracts protecting confidential project information
- Why it matters: Safeguards sensitive plans or trade secrets
- Who creates it: Legal teams
- Who signs it: Contractors, subcontractors, or clients
- Customization: Standard with case-specific clauses

15. Lien waivers
- What it is: Documents waiving the right to file a lien after payment is received
- Why it matters: Prevents legal disputes and ensures timely payments
- Who creates it: Legal or finance teams
- Who signs it: Contractors or suppliers
- Customization: Standard with project-specific amounts
16. Performance bonds
- What it is: Guarantees that a contractor will fulfill their contractual obligations
- Why it matters: Protects clients from project delays or failures
- Who creates it: Bond providers or legal teams
- Who signs it: Contractors
- Customization: Standardized terms with project-specific guarantees
17. RFI (Request for Information) forms
- What it is: Requests for clarification or additional details on a project
- Why it matters: Ensures smooth communication and accurate execution
- Who creates it: Contractors or subcontractors
- Who signs it: Recipients acknowledging receipt
- Customization: Specific to the question or issue
18. Joint venture agreements
- What it is: Contracts between two companies collaborating on a project
- Why it matters: Clearly defines roles, responsibilities, and profit-sharing
- Who creates it: Legal teams or stakeholders
- Who signs it: Representatives of both companies
- Customization: Tailored to the joint project
Read also: What is contract management? A complete guide
19. Material delivery forms
- What it is: Documents confirming the receipt of construction materials
- Why it matters: Ensures accountability and accurate inventory
- Who creates it: Suppliers or site supervisors
- Who signs it: Delivery personnel and supervisors
- Customization: Standard format with delivery-specific details
20. Project closeout documents
- What it is: Final paperwork confirming project completion
- Why it matters: Provides a record of project fulfillment and releases liability
- Who creates it: Project managers or contractors
- Who signs it: Contractors, clients, and inspectors
- Customization: Standardized with project-specific summaries
Building smarter with digital contracts
Implementing digital contracts can speed up approvals, improve accuracy, and enhance collaboration, all while staying compliant. This is especially critical within an industry where every second and detail matters.
Adopting digital contracts doesn’t just streamline paperwork, it builds the foundation for smarter constructions where projects run smoother, teams communicate better, and deadlines are met faster.